Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Disease: What You Need to Know
- Dr. Fedinand Getankwa

- May 6, 2025
- 3 min read
When your gut isn’t happy, your whole body feels it. Inflammatory Bowel Disease, or IBD, is one of those chronic conditions that can turn everyday life into a daily struggle. It affects millions of people around the world, yet many still don’t fully understand what it is, how it works, or how it’s treated. This article breaks it down in simple terms to help you or someone you care about make sense of IBD.
What Is Inflammatory Bowel Disease?
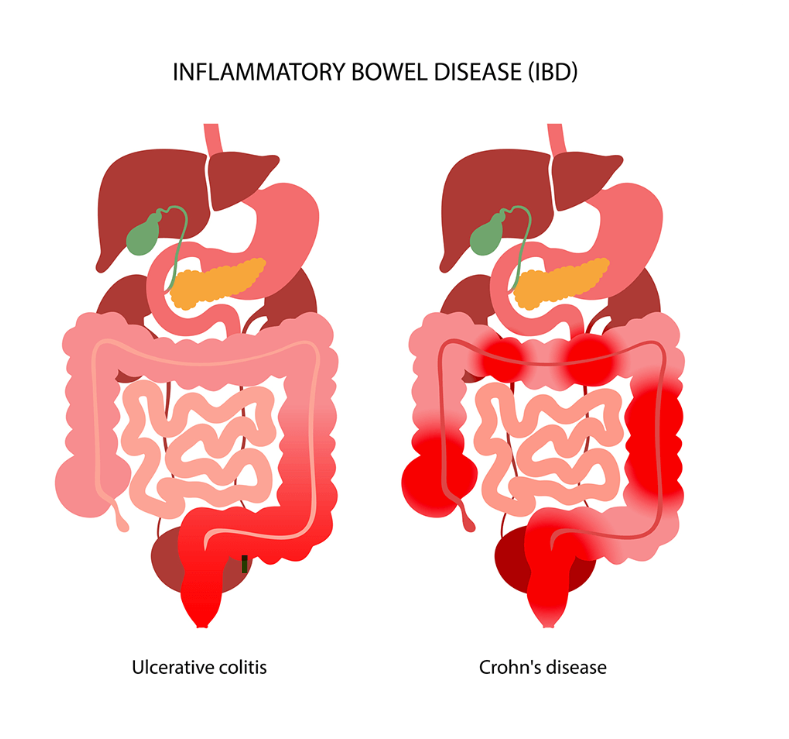
Inflammatory Bowel Disease is an umbrella term for disorders that cause chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. The two main types are:
Crohn’s disease, which can affect any part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, from the mouth to the anus, but most commonly impacts the small intestine.
Ulcerative colitis, which is limited to the colon (large intestine) and rectum.
Despite their differences, both conditions involve an overactive immune response that mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the digestive tract, leading to inflammation, ulcers, and other damage.
Common Symptoms
IBD symptoms can vary from person to person, and they may come and go over time. During a “flare-up,” symptoms can be intense, while in remission, they may disappear for weeks or months.
Typical symptoms include:
Persistent diarrhea
Abdominal pain and cramping
Fatigue
Weight loss
Blood in the stool
Urgency to have a bowel movement
Some people may also experience joint pain, skin rashes, or eye inflammation, since IBD can affect more than just the gut.

What Causes IBD?
The exact cause of IBD is still unknown, but several factors seem to play a role:
Genetics: People with a family history of IBD are at higher risk.
Immune system issues: A misfiring immune response may trigger inflammation in the digestive tract.
Environmental triggers: Smoking, diet, stress, and certain infections can worsen symptoms or trigger flare-ups.
It's important to note that IBD is not caused by what you eat, though some foods may aggravate symptoms during flares.
How Is IBD Diagnosed?
Because symptoms of IBD can overlap with other digestive disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), diagnosis often involves a combination of tests:
Blood tests and stool samples to look for signs of inflammation or infection
Colonoscopy or endoscopy to view the inside of the digestive tract
Imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs to assess damage and inflammation
Getting a correct diagnosis is the first step in managing the condition effectively.
Treatment and Management
There’s no cure for IBD, but it can be managed with a combination of:
Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immune system suppressors, and biologics can reduce inflammation and prevent flare-ups.
Diet and nutrition: While no one-size-fits-all diet exists, many patients benefit from working with a nutritionist to find trigger foods and maintain good nutrition.
Surgery: In severe cases, removing parts of the intestine may be necessary if other treatments fail.
Lifestyle changes, stress management, and regular medical care are also key parts of living well with IBD.
Living With IBD
A diagnosis of IBD can feel overwhelming, but many people go on to lead full, active lives. The key is staying informed, working closely with healthcare providers, and being proactive about symptoms and flare-ups.
Support from family, friends, and even online communities can also make a big difference. You’re not alone—and with the right tools and mindset, IBD can be a manageable part of life, not the center of it.



Comments